(Geo)spatial Statistics with R (Meuse)
In this exercise, we will explore the concepts and applications of Deterministic and Stochastic Interpolation Methods.
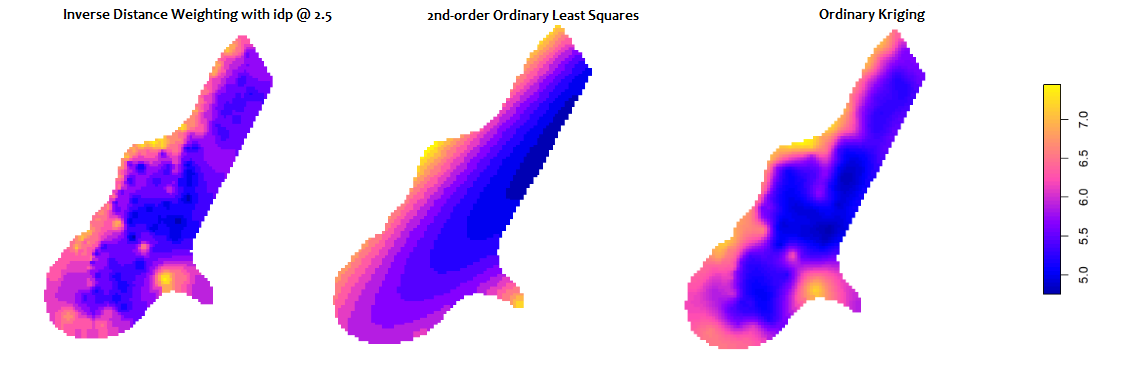
We traverse such technics as:
1) Deterministic methods
a. Thiessen polygons
b. Linear Regression
c. Inverse Distance Weighting
d. Ordinary Least Squares
2) Stochastic methods
a. Variograms and Kriging
3) we also briefly highlight ways we can interrogate the quality of an interpolation with;
a. N-fold cross validation; and
b. Residual Mean Squared Error (rmse).
For this assignment we use a dataset that is well-suited to illustrate these concepts. The meuse dataset which comes with the gstat package. meuse: gives locations (on a regular grid) and topsoil heavy metal concentrations, along with a number of soil and landscape variables at the observation locations, collected in a flood plain of the river Meuse, near the village of Stein (NL). Heavy metal concentrations are from composite samples of an area of approximately 15 m x 15 m.